3D Scanning & Reverse Engineering Services
What is Reverse Engineering?
Reverse engineering is a process that involves documenting the current state of a physical object and reconstructing it as a 3D model to recover the design intent. A perfect reconstruction of the original design, in terms of simple analytical surfaces (planes, cylinders, etc.) and freeform surfaces (NURBS) to produce a new reference CAD model.
Why Choose 3D Scanning?
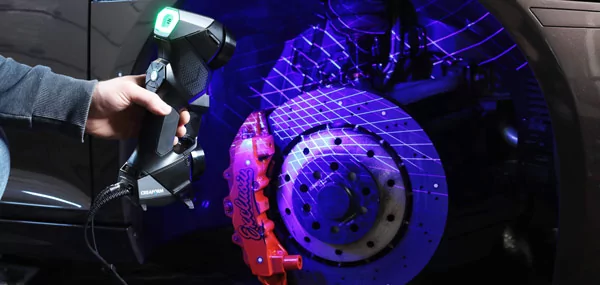
- High level of detail: With a high resolution for intricate details and full-color support, ARY’s 3D scanning cloud quality is impeccable for reverse engineering, modeling freeform surfaces and showing even the smallest features.
- Versatility: With ARY’s advanced laser and optical technologies and limitless scanning volumes, our drafting and design team can measure any part, regardless of size, shape, material, surface finish, and complexity.
Simplicity: We arrive on-site, scan the part, and provide you with a deliverable in the format of your choice.
Speed: Unlike a point cloud, the generated mesh is already lightened and processed by our internal team, ready to be integrated seamlessly into your preferred reverse engineering, CAD, or 3D printing software.
Creating Trusted References: An study commissioned by the United States Department of Justice found that “3D scanning has facilitated successful prosecutions, multiagency collaboration and communication, valuable crime-scene perspectives for juries, and faster scene processing with an upgraded device.”
3D Scanning Details
- Accuracy
- 0.04 mm
- Volumetric Accuracy
- 0.04+0.06 mm/m
- 3D Scanning Rate
- 1,200,000 points/s, 20FPS
- Integrated Photogrammetry and Texture Scanning
- Output formats
- OBJ, STL, ASC, PLY, P3, 3MF, and many more!
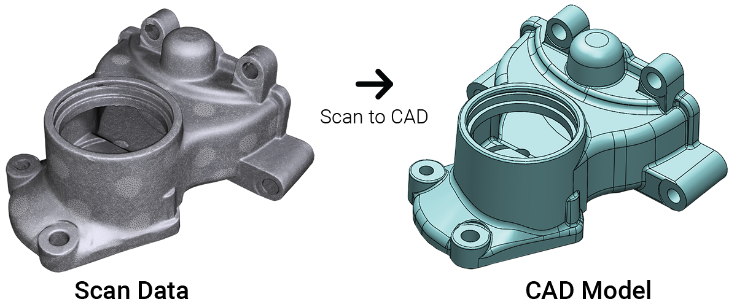
3D Scanning Applications
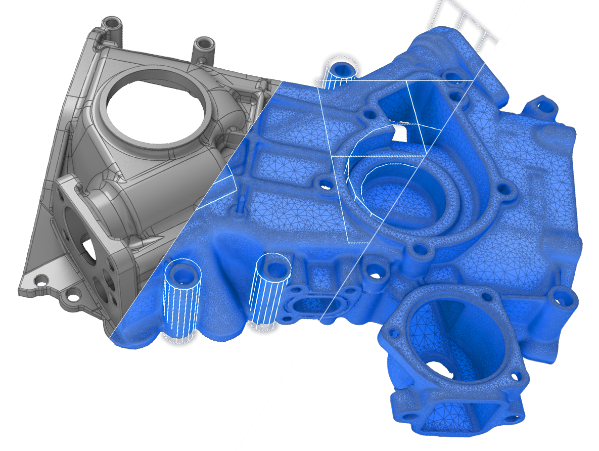
- Reverse engineering – developing replacement custom parts
- Quality control – 3D scanning incoming parts and equipment for tolerance inspection
- Tooling design
- Prototyping and 3D printing – creating carbon copies of an existing object
- Documentation – capturing a reference before changes are made to an object
- Any area where large amounts of rapid data capture are necessary for complex objects
- Performing a contour-match for non-linear shape assemblies
